Contents
I. Quotation Categories
II. Quotation Methods
III. Quotation Rules
IV. Quotation Rule Check
V. Departmental factor
Quotation is a final price obtained by linking quotation objects with quotation rules through quotation categories. On this basis, quotation of different situations can also be achieved through Departmental factor and quotation methods.
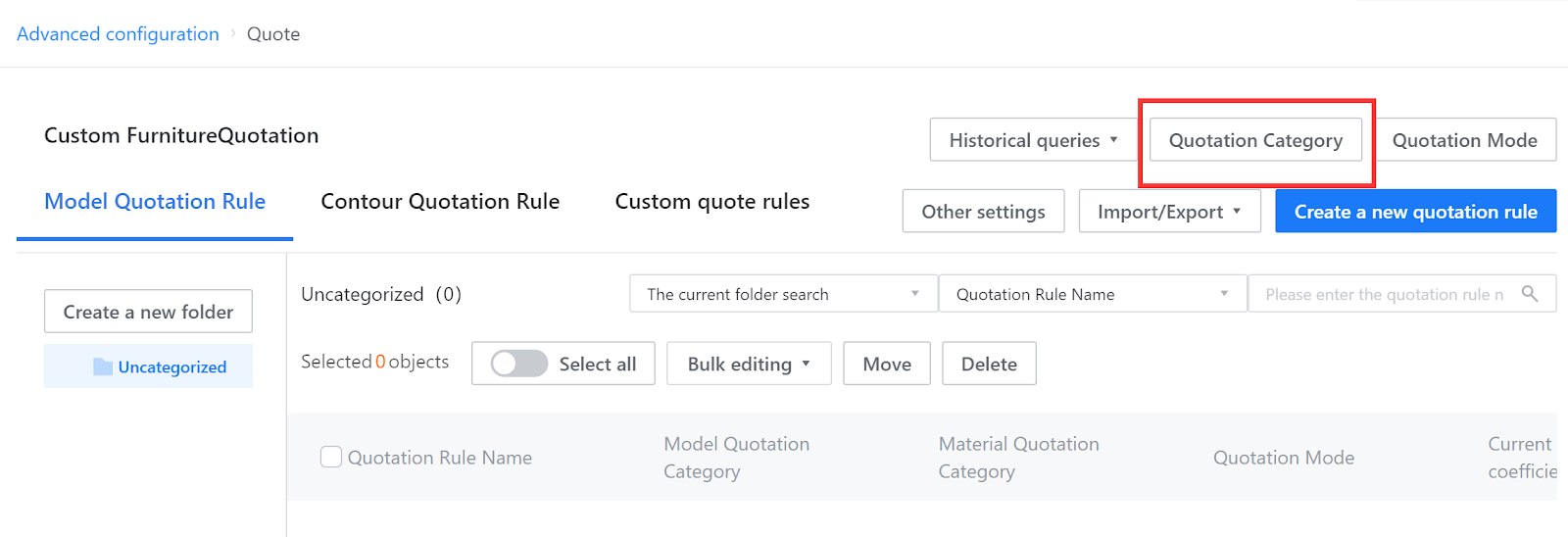
I. Quotation Categories
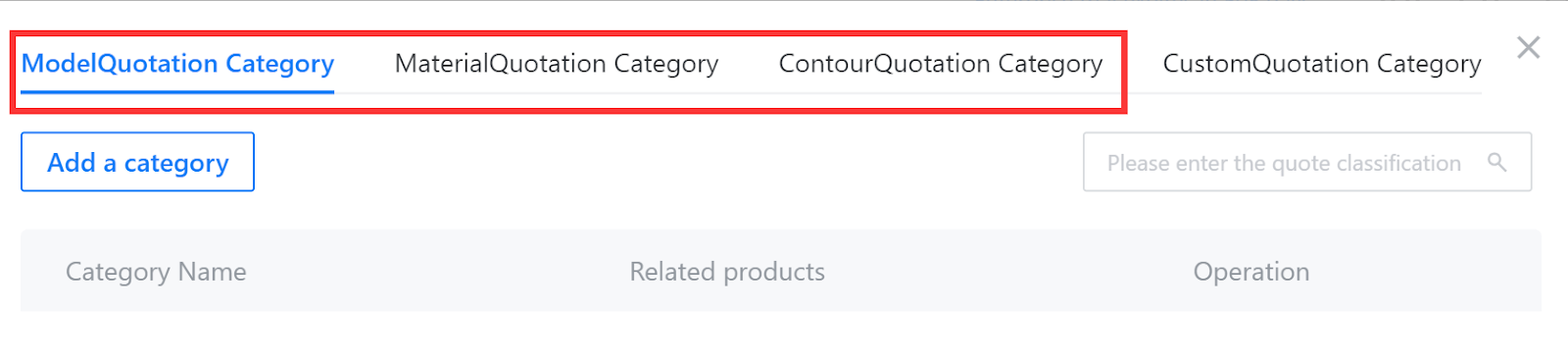
Add a quotation category, and assign it to the quotation object. Select this quotation category when writing quotation rules, and assign quotation rules to the quotation object through the quotation category. According to the different quotation objects, the quotation is divided into:
-
Model quotation category: categorization of parameterized models.
-
Contour quotation category: categorization of contour lines, including crown, toekick, light rail moldings, and countertops.
-
Material quotation category: categorization of texture mapping.
Model quotation category: categorization of parameterized models.
Contour quotation category: categorization of contour lines, including crown, toekick, light rail moldings, and countertops.
Material quotation category: categorization of texture mapping.
II. Quotation Methods
Used when multiple quotation methods are required for the same quotation object (quotation by width, quotation by projected area, etc.). For example, if a cabinet can be priced by both width and projected area, quotation methods are needed. That is, multiple quotation rules can be created for the same quotation object according to the required number of quotation methods. In the project, you can choose the desired quotation method.
-
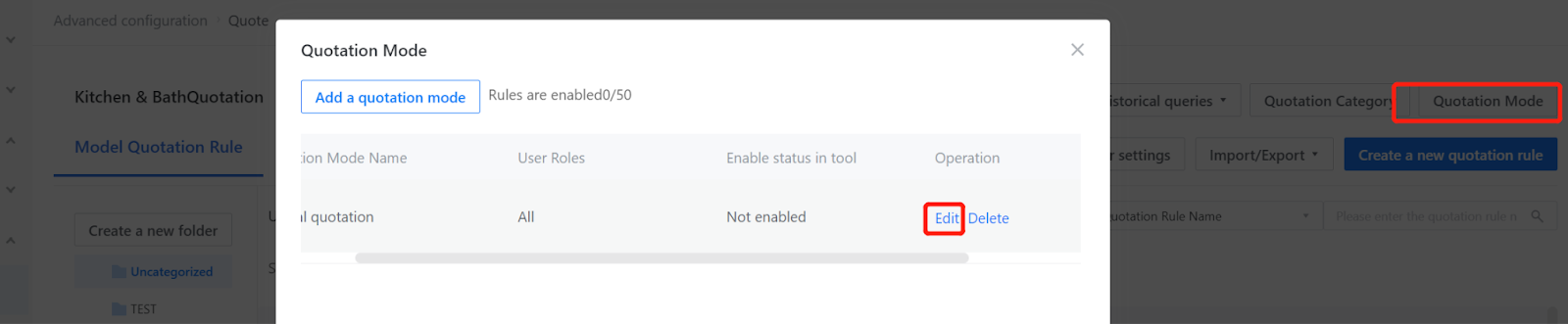
Quotation Method Editing
Quotation Method Editing
In the quotation method editor, quotation methods can be added. Whether to display in the tool and which quotation method is default can be selected. There is no limit to the number of quotation methods that can be created, but only four can be displayed in the tool at most.
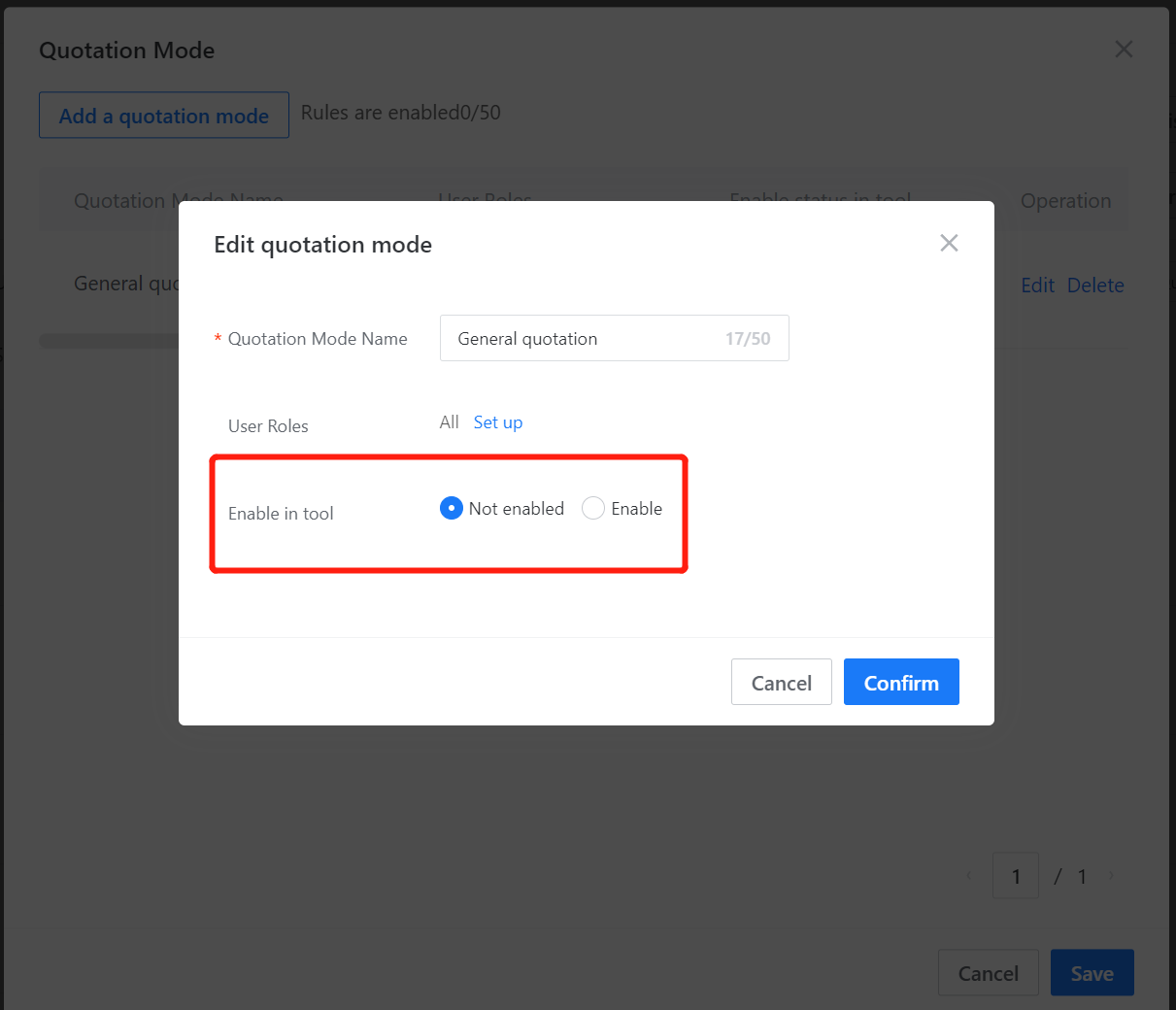
Real-time quotation can be seen in the lower right corner of the tool, priced according to the default quotation method. And other quotation methods can be selected.
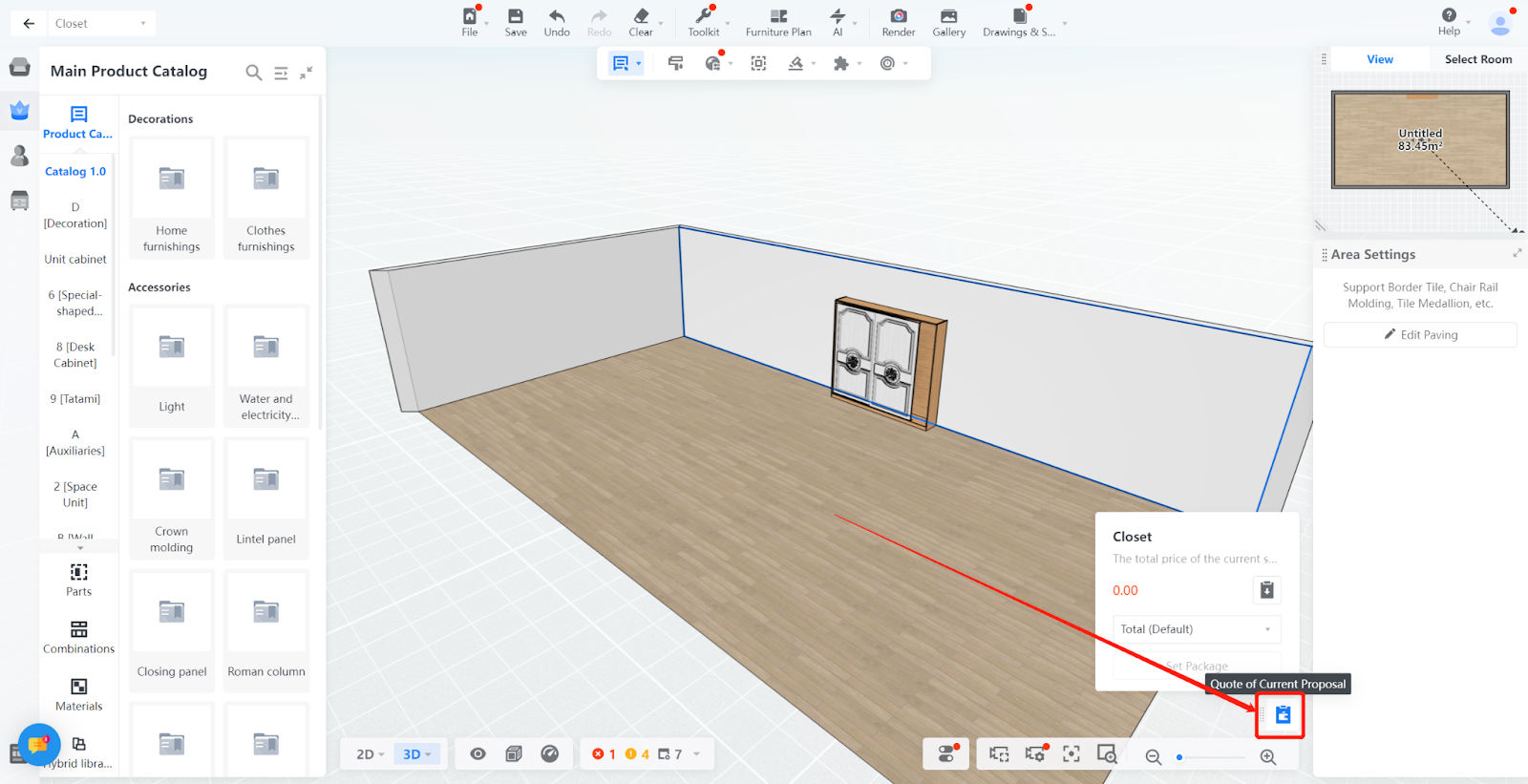
When downloading the quotation list, the quotation method can also be selected to choose which quotation method to display in the list.
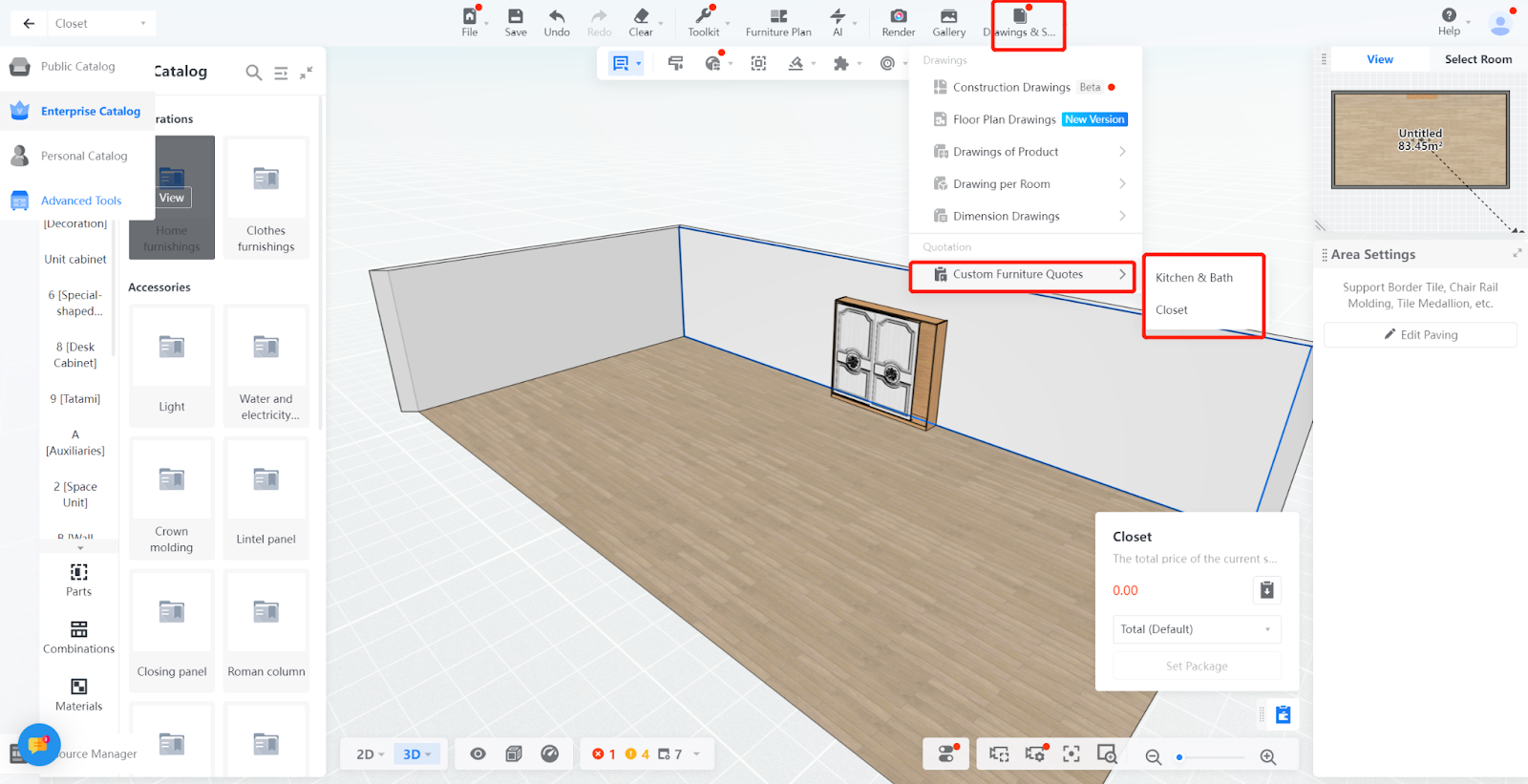
-
Associated quotation Methods
Associated quotation Methods
When writing quotation rules, associating quotation methods is required, and by default, all quotation methods apply. If multiple quotation methods can be used, create multiple quotation rules (model/contour quotation categories are the same as material quotation categories). “All” means that no matter what quotation method is chosen, this quotation rule will be calculated. quotation rules cannot be defined repeatedly in the same category (category combination). Create an associated quotation method and select a specific quotation method for quotation rules, and you can also create other associated quotation methods for the same quotation category. However, if “all” is selected, specific quotation methods cannot be created again because “all” includes all methods, and creating specific methods again would be repetitive.
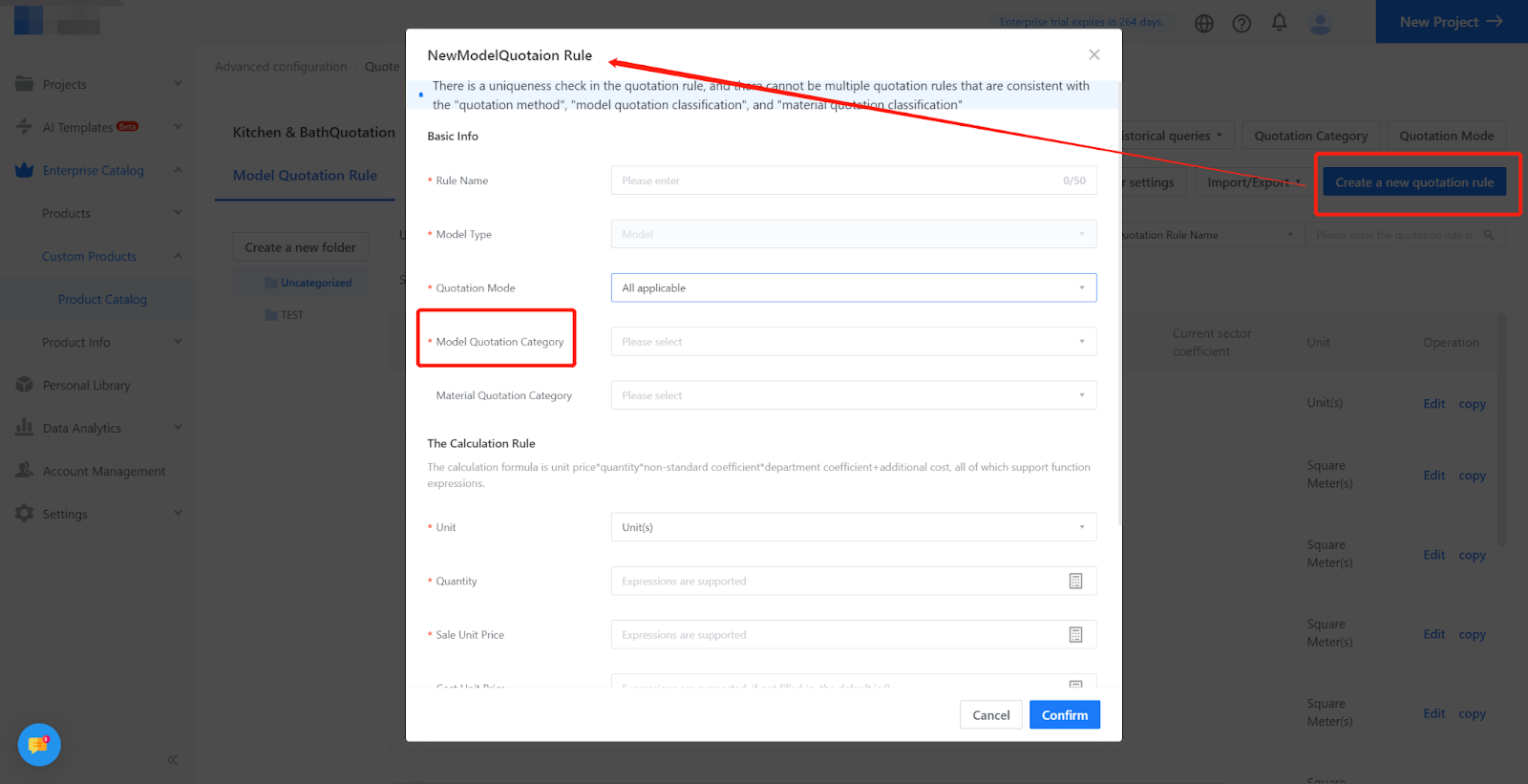
III. Quotation Rules
-
Quotation rules are divided into model quotation rules and contour quotation rules.
Quotation rules are divided into model quotation rules and contour quotation rules.
-
Model quotation rules: quotation rules applied to parameterized models.
-
Contour quotation rules: quotation rules applied to contour lines.
Model quotation rules: quotation rules applied to parameterized models.
Contour quotation rules: quotation rules applied to contour lines.
2. Setting method: A model quotation rule is composed of a model classification + material classification (optional).
A contour quotation rule is composed of a contour classification and material classification (optional).
Note: quotation rules cannot be defined repeatedly in the same category (category combination).
3. The final price of the model = unit price*quantity*non-standard coefficient + additional fee.
Quotation Name: Refers to the name of the current quotation rule, which may not be the same as the quotation category name.
Selection Type: Model quotation is not modifiable, and contour quotation can choose the corresponding type.
Material quotation categories may or may not be optional. When the model quotation is related to the material, quotation rules need to be set separately; otherwise, it is not necessary to choose.
Unit Price: It can be filled with formulas or constants, and judgment conditions are supported. The cost unit price is currently only used for API output and does not affect the quotation in the tool.
Quantity: It can be filled with formulas or constants. Note that the WDH referenced in the quotation calculation formula corresponds to the output width, depth, and height of the model, not the physical width, depth, and height of the model. The output width, depth, and height can be customized according to the actual situation; the unit in the editor is MM, and the quotation unit is M. Pay attention to unit conversion when using.
Non-standard Coefficient: Refers to the coefficient multiplied on the basis of the original value, which defaults to 1 if not filled in.
Additional Fees: Additional fees are added on top of the existing fees, and process, labor, and other costs can be written here.
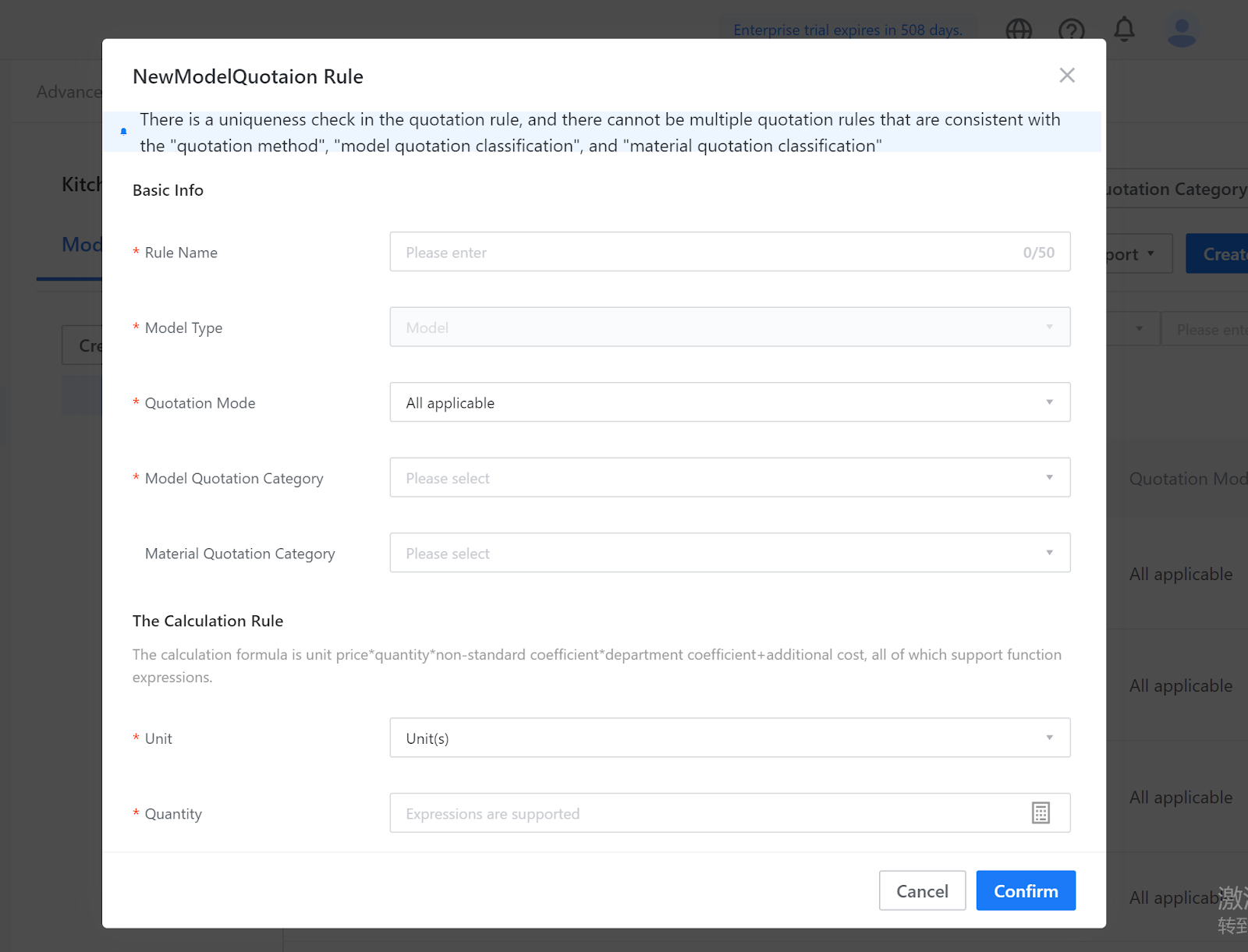
IV. Quotation Rule Check
Quotation rules involve formula calculations, quotation categories, and quotation objects, which are prone to errors. To prevent situations where the tool discovers quotation problems and returns to modification, verification can be used to check whether quotation rules are correct on the quotation settings page.
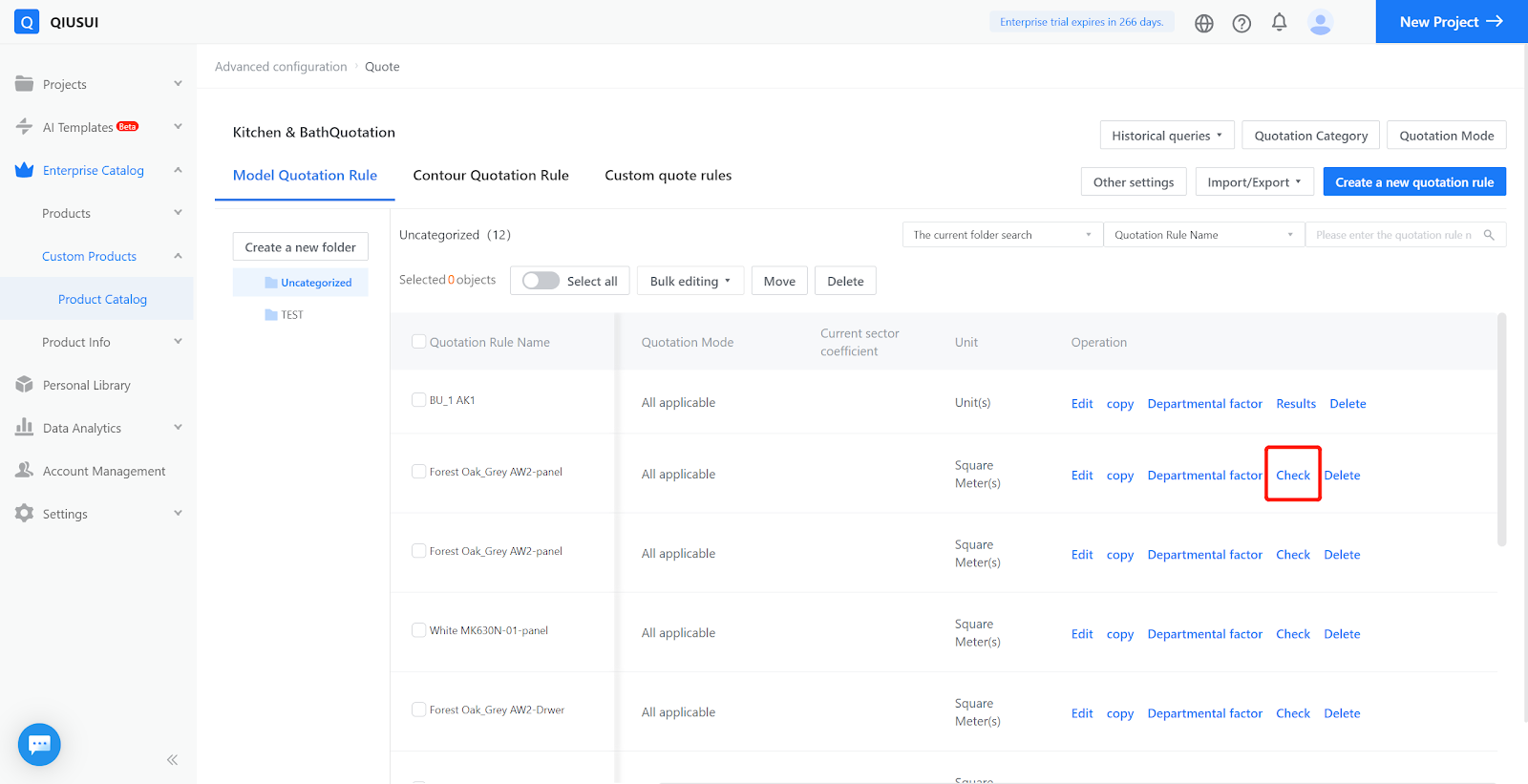
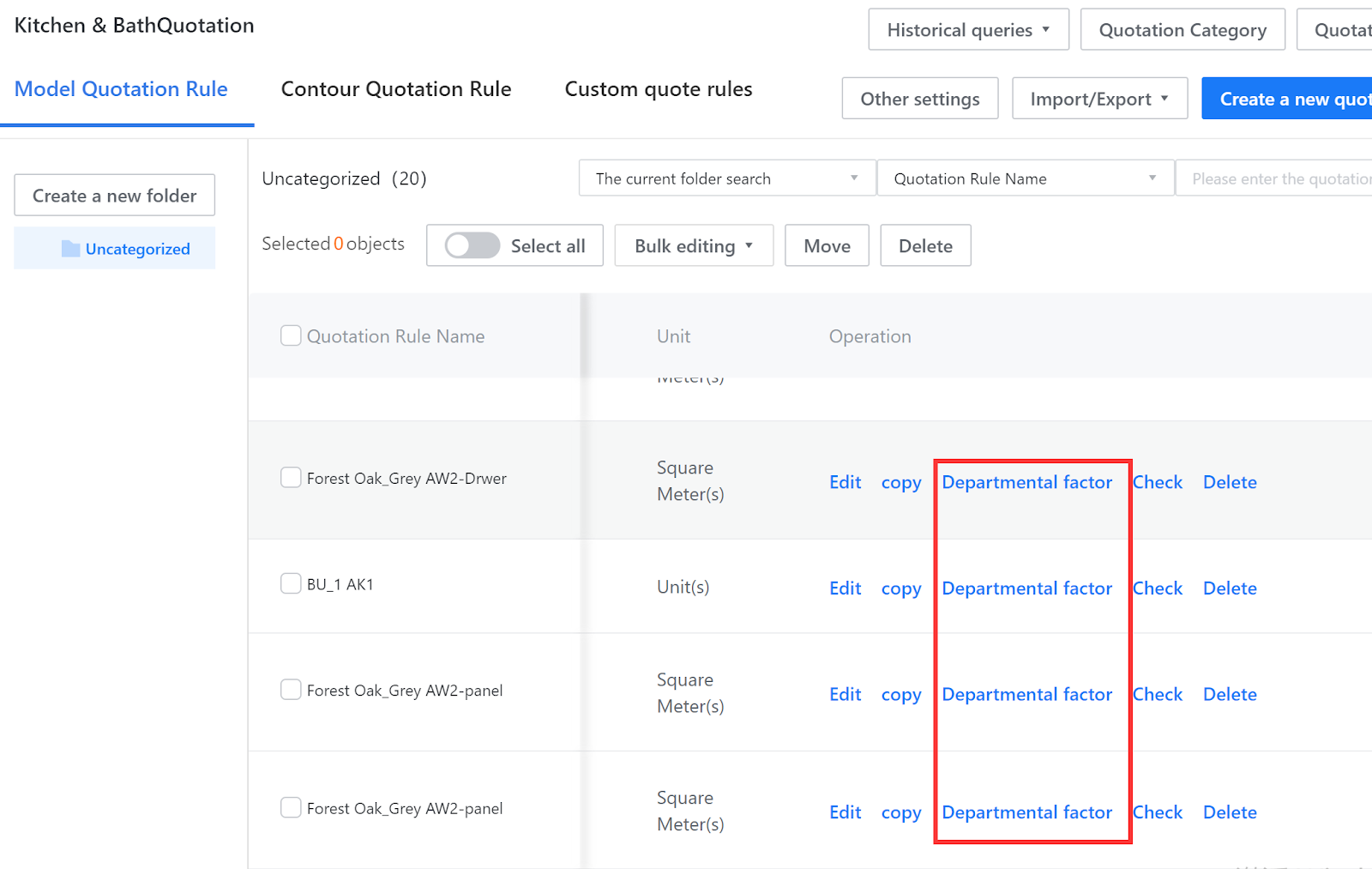
V. Departmental factor
Due to differences in consumer levels in different cities, product prices also differ. Departmental factor are mainly used to handle these differences and can also be used for other scenarios that require quotation based on account impact (promotions).
First, assign sub-accounts to groups in the sub-account management, and then allocate different systems to different groups through Departmental factor or batch editing of Departmental factor in quotation rules.
Set start and end times and Departmental factor. The group coefficient will only take effect within the effective time range. After setting the group coefficient, it will be multiplied by the quotation rule calculation result.